Articles in the ‘Beginner’ category Page 14
-
The building blocks of Chinese, part 4: Learning and remembering compound characters
The key to learning Chinese compound characters is to learn the building blocks and how they fit together, including both the function of each component and the structure of the compound. Add some clever memory techniques and you’ll be able to dramatically increase the speed and efficiency of your learning!
Read → -
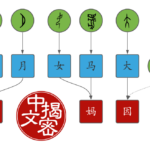
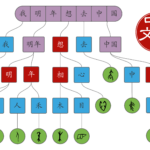
The building blocks of Chinese, part 3: Compound characters
A vast majority of Chinese characters are compounds, and understanding how the components fit together and which function they have, will make learning and remembering characters a lot easier. This article explains the most important types of compounds you’ll encounter and how you can use that knowledge to learn characters more easily.
Read → -
Using voice messaging as a stepping stone to Chinese conversations
Being able to have a conversation is a goal for most students of Chinese, be it with loved ones, for professional purposes or for travel, but what if you think conversations are too scary, too difficult or just impractical? Try using voice messaging as a stepping stone to better conversations in Chinese!
Read → -
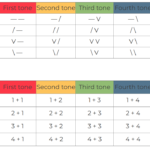
A smart method to discover problems with Mandarin sounds and tones
It’s often hard to assess one’s own pronunciation when learning Mandarin. People around you might understand what you are saying, but that doesn’t necessarily mean your tones are good. Simply asking people if your pronunciation is good won’t work either, because they will often tell you that your pronunciation is good even if it’s not. So how can you find out how good your pronunciation really is?
Read → -
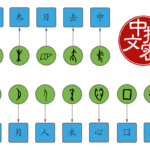
The building blocks of Chinese, part 2: Basic characters, components and radicals
Most Chinese characters are compounds consisting of two or more components, but some components are in themselves compounds that can be further broken down. But how do you know where to stop? And how do you learn and remember the most basic building blocks?
Read → -
The building blocks of Chinese, part 1: Chinese characters and words in a nutshell
Learning to read and write Chinese is a daunting task, but the challenge becomes more manageable if you focus on learning the building blocks, learning how components form characters and how characters form words. This article is the first part in a series helping adult students make sens of Chinese characters.
Read → -
Hacking Chinese Podcast one-year anniversary Q&A
How do you study Chinese when you’re busy with other things? How do you cope with a Chinese course that is too hard for you? And are translated texts okay to use for reading practice?
Read → -
Chinese language logging, part 3: Tools and resources for keeping track of your learning
Logging you language learning can be very useful, and there are many tools and resources out there to help you, but which are the best and how do you use them?Logging you language learning can be very useful, and there are many tools and resources out there to help you, but which are the best and how do you use them?
Read → -
Chinese language learning in the twenty-first century: Towards a digital ecosystem? Interview with Julien Leyre
Digital resources have made learning Chinese considerably easier than it used to be, but another problem has appeared: How can we make sense of and navigate the vast number of resources and find what’s best for us?
Read → -
The new HSK 3.0: What you need to know
On July 1st, 2021, a new Chinese proficiency standard takes effect. This will have big consequences for the HSK, the most widely used proficiency test for non-native speakers. What are these changes and what do they mean for you as a student?
Read →