Articles tagged with ‘Tones’ Page 2
-
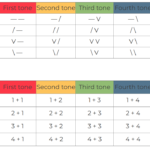
7 ways to write Mandarin tones
There are many ways of writing down the tones of Mandarin beyond the standard tone marks. Which are they and what pros and cons do they have for learners?
Read → -
A smart method to discover problems with Mandarin sounds and tones
It’s often hard to assess one’s own pronunciation when learning Mandarin. People around you might understand what you are saying, but that doesn’t necessarily mean your tones are good. Simply asking people if your pronunciation is good won’t work either, because they will often tell you that your pronunciation is good even if it’s not. So how can you find out how good your pronunciation really is?
Read → -
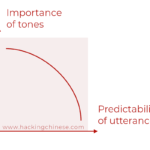
The importance of tones is inversely proportional to the predictability of what you say
Tones in Mandarin carry roughly as much information as vowels do, but still some people insist that tones are not very important, or even that native speakers don’t really use tones. Why is that and what can we learn from digging deeper into this misconception?
Read → -
Learning the second tone in Mandarin Chinese
Many students of Chinese struggle with the third tone, but almost as many also have problems with the second tone. So how should the second tone be pronounced, and what are the most common learner errors?
Read → -
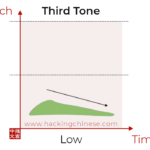
Learning the third tone in Mandarin Chinese
The third tone in Mandarin is the most mispronounced of all. It’s an essentially low tone, but many learners are unaware of this, partly because the way the tone is taught is flawed. Don’t think of it as a falling-rising tone, just think of it as a low tone!
Read → -
The most serious mistake students make when learning Mandarin pronunciation
Learning to hear and say the sounds of Mandarin can be tricky, but it’s made much more difficult by the way many students go about it. By focusing on reading over listening, they are making themselves a big disservice!
Read → -
Does using colour to represent Mandarin tones make them easier to learn?
Some learning materials, apps and tools allow you to add colours to show Mandarin tones, but is this really helpful? This article discusses the ins and outs of using colour to learn and remember tones, along with some practical considerations.
Read → -
Training your Chinese teacher, part 3: Listening ability
Listening ability is generally overlooked in language teaching. At first glance, it might seem that having a teacher is not as useful for improving listening as it is for improving speaking, but is that really the case? This article covers both what you should and what you shouldn’t do with your teacher if improving listening ability is your goal!
Read → -
How good is voice recognition for learning Chinese pronunciation?
Speech recognition technology has developed rapidly and can now be relied on to correctly identify standardised and clear pronunciation in Mandarin. But can it be used to check your Mandarin pronunciation? Not necessarily. This article looks at how well speech recognition software deals with non-native and low-quality audio, focusing on the question if speech recognition is too lenient for pronunciation practice.
Read → -
Using speech recognition to improve Chinese pronunciation, part 1
Speech recognition technology has developed rapidly and can now be relied on to correctly identify standardised and clear pronunciation in Mandarin. But can it be used to check your Mandarin pronunciation? Not necessarily. There are two problems that need to be investigated to answer that question. This article looks at the first: If speech recognition is unable to identify what you say, does that mean that your pronunciation is bad, or could it be the speech recognition that isn’t good enough?
Read →